Breaking News
Popular News




Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
Polkadot (DOT) is more than just another blockchain—it’s a next-generation Web3 protocol designed for interoperability, scalability, and decentralization. As crypto evolves in 2025, Polkadot continues to stand out by offering solutions to real problems plaguing fragmented networks.
In this guide from bit2050.com, we break down Understanding Polkadot (DOT) through 7 essential features that make it a top-tier Layer 0 blockchain.
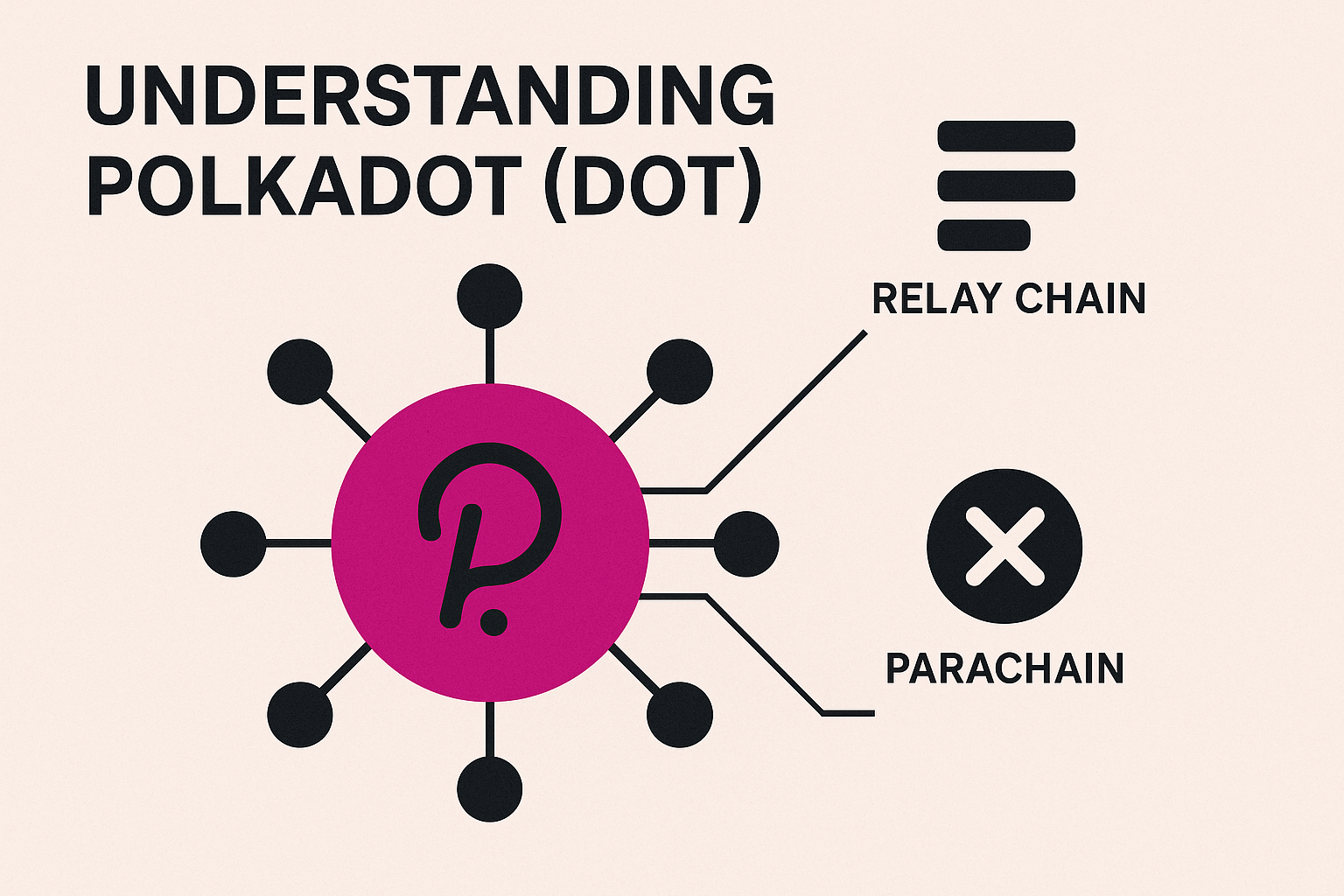
Polkadot is not a Layer 1 like Ethereum or Solana—it’s a Layer 0 protocol that connects multiple Layer 1 chains (called parachains).
Think of it as the internet of blockchains
Enables custom blockchains to communicate securely and efficiently
Parachains are independent Layer 1 chains connected to the Polkadot Relay Chain.
Each parachain can have its own token, governance, and logic
They benefit from Polkadot’s shared security model
Examples: Acala, Moonbeam, Astar Network
Polkadot provides pooled security across its ecosystem.
Validators secure the Relay Chain and all connected parachains
Projects don’t need to bootstrap their own validator sets
Ensures lower entry barrier for new blockchains
One of Polkadot’s key innovations is XCMP (Cross-Chain Message Passing).
Allows parachains to talk to each other
Enables complex multi-chain dApps and DeFi protocols
Eliminates the need for centralized bridges
Polkadot uses transparent, decentralized governance:
DOT holders can propose upgrades and vote on changes
Referenda decide protocol improvements democratically
All governance is handled on-chain, without hard forks
Polkadot supports forkless upgrades via on-chain governance and runtime upgrades.
Smart contract updates, bug fixes, and new features can be added seamlessly
This minimizes network splits and user disruption
The DOT token powers the Polkadot ecosystem through:
Staking – to secure the network
Governance – to vote on decisions
Bonding – to connect new parachains
Gas Fees – on the Relay Chain
As Polkadot expands, DOT’s utility continues to grow.
Moonbeam – EVM-compatible smart contracts
Acala – DeFi hub and stablecoin protocol
Astar – Multi-chain dApp hub
Phala Network – Privacy-preserving smart contracts
Centrifuge – Real-world asset tokenization
A: Unlike Ethereum, Polkadot is a Layer 0 chain that connects and secures multiple blockchains, allowing each to operate independently while being interoperable.
A: DOT remains a top 15 crypto project with long-term potential due to its unique architecture and expanding ecosystem.
A: A parachain slot gives a blockchain project the right to connect to Polkadot’s Relay Chain. These are acquired through parachain auctions.
A: Yes. Through bridges and cross-chain protocols, Polkadot can communicate with other chains, including Ethereum, via projects like Snowfork and LayerZero.
A: DOT holders propose and vote on changes via referenda, making Polkadot one of the most community-driven blockchain projects.
Polkadot isn’t just another blockchain—it’s a Web3 enabler. By solving the trilemma of scalability, security, and interoperability, it lays the foundation for a decentralized multichain future. As 2025 unfolds, understanding Polkadot (DOT) is essential for anyone serious about blockchain innovation.
For more in-depth crypto education and trend analysis, visit bit2050.com — your #1 resource for blockchain’s next frontier.