Breaking News
Popular News




Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
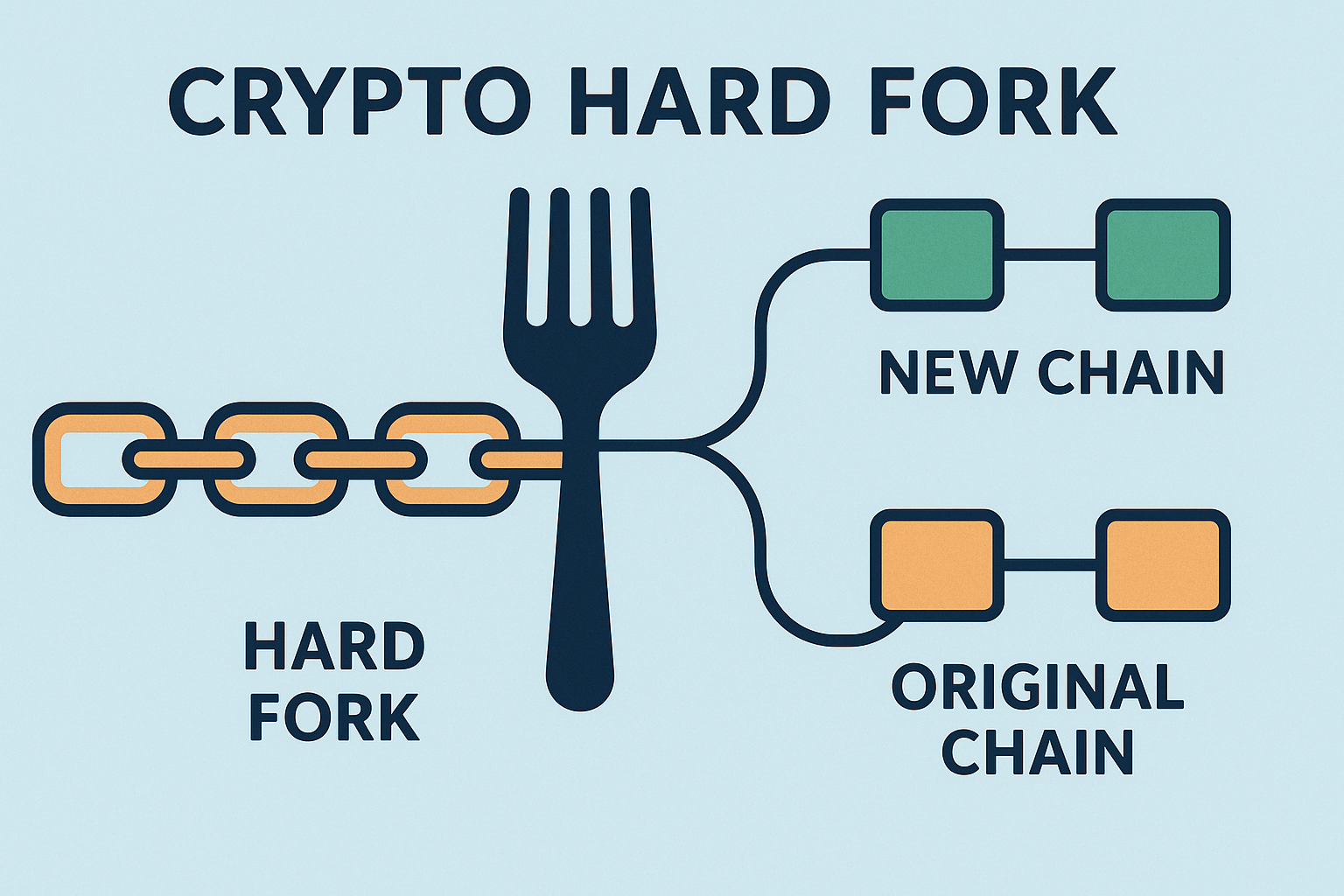
If you’ve heard about Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum Classic, or the Shanghai upgrade and wondered what they mean, you’re not alone. These events are all examples of hard forks — major changes in a blockchain’s rules.
At bit2050.com, we break down what is a crypto hard fork, how it works, and why it plays a critical role in the evolution of cryptocurrencies.
A crypto hard fork occurs when a blockchain splits into two separate chains due to a disagreement or major upgrade in the protocol. This results in:
Two blockchains with a shared history
Two different sets of rules going forward
Potentially two different coins
In short, a hard fork is like a divorce in code — one chain becomes two, and each goes its own way.
Once a hard fork happens, nodes running the old software can’t validate new blocks. That’s why all participants must upgrade to stay on the new chain.
Some forks are planned and agreed upon (e.g., Ethereum’s Shanghai upgrade). Others are contentious (e.g., Bitcoin vs Bitcoin Cash in 2017).
✅ Planned forks = smoother transitions
❌ Controversial forks = community splits
Examples include:
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) — forked from Bitcoin (BTC)
Ethereum Classic (ETC) — forked from Ethereum after the DAO hack
Bitcoin SV (BSV) — forked from Bitcoin Cash
✅ If you held the original coin before the fork, you might receive free coins on the new chain.
Reasons for hard forks include:
Fixing bugs or vulnerabilities
Upgrading scalability
Changing consensus mechanisms
Reversing hacks (as with the DAO)
Think of it as a “software upgrade with consequences.”
Forks can cause price volatility because:
Traders speculate on the new coin
Confusion about which coin is “real”
User confidence may shift
📉 Market dynamics often change rapidly during major forks.
For a smooth fork:
Developers, miners, and validators must agree
Wallets and exchanges must support the new chain
Users should back up wallets and follow official guides
Without agreement, the chain may split into rivals, like BTC vs BCH.
Soft Fork: A backward-compatible upgrade. Old nodes still work.
Hard Fork: A non-compatible split. New rules reject old blocks.
Soft forks are like rule tweaks. Hard forks are full-on system changes.
A: You typically retain your coins on both chains. For example, 1 BTC before the fork = 1 BTC + 1 BCH after the fork (if supported by your wallet/exchange).
A: Yes, if you want to interact with the new chain. Always follow official upgrade instructions to avoid loss.
A: It depends. Some forks lead to improvements (like Ethereum’s upgrades), while others cause community fragmentation.
A: Yes — in rare cases, such as Ethereum’s fork to reverse the DAO hack. But this is extremely controversial.
A: A hard fork splits the blockchain. An airdrop simply distributes tokens, often on the same chain.
Now that you understand what is a crypto hard fork, you’re better prepared to navigate protocol changes, governance drama, and new coin opportunities. Whether it’s Bitcoin splitting in 2017 or Ethereum evolving post-Merge, forks shape the future of Web3.
Stay ahead of major forks, crypto upgrades, and blockchain trends at bit2050.com — your #1 resource for decentralized innovation.