Breaking News
Popular News




Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
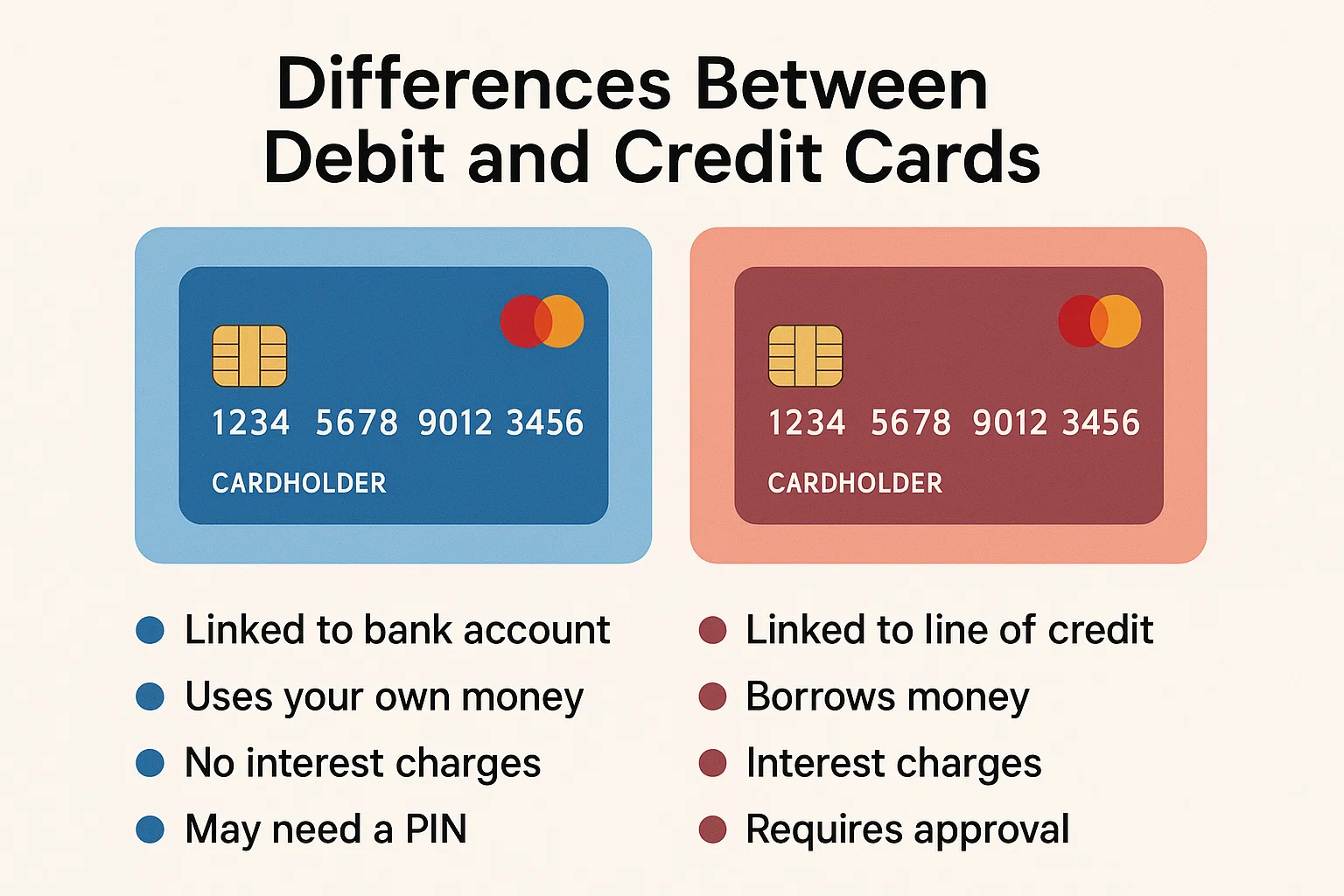
In the age of cashless transactions, understanding the differences between debit and credit cards is essential. Both plastic cards may look identical but serve entirely different financial functions.
Whether you’re a student, working professional, or entrepreneur, this guide from bit2050.com will help you make informed decisions.
Debit Card: Spends money directly from your bank account.
Credit Card: Uses borrowed money from the bank (credit limit).
Debit: No bill. Money deducted immediately.
Credit: Monthly bill generated. Repayment needed by due date.
Debit: No interest since you’re spending your own money.
Credit: Interest applied if dues are unpaid after the grace period.
Debit: No risk of going into debt (unless account overdrawn).
Credit: High risk of debt if you overspend and don’t repay on time.
Debit: Basic or limited reward programs.
Credit: Higher rewards, cashback, travel points, lounge access, etc.
Debit: Limited protection in case of fraud.
Credit: Better protection under consumer liability laws.
Debit: No impact on credit history.
Credit: Directly affects your CIBIL or credit score based on usage and repayments.
Credit cards are usually safer due to better fraud protection and dispute mechanisms.
You can pay using a credit card, but you’ll need to repay the amount later with or without interest.
Only credit cards affect and help build your credit score.
Yes. Since they deduct money directly from your bank, there’s no interest involved.
Yes, but credit card withdrawals involve extra fees and interest, while debit card withdrawals are generally free up to a limit.
Understanding the differences between debit and credit cards empowers you to manage your money better. Choose the card based on your financial habits, goals, and responsibility level. For more such comparisons and smart money tips, visit bit2050.com.